√完了しました! sinus bradycardia with unifocal ventricular bigeminy 251628-Sinus bradycardia with unifocal ventricular bigeminy
This encounter shows a fast rate over 100 bpm, with a regular rhythm and P waves, indicating sinus tachycardia The extremely long delay between the P wave and QRS indicates first degree heart block Additionally, ectopy is seen in this encounter, in the form of premature ventricularA premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is a relatively common event where the heartbeat is initiated by Purkinje fibers in the ventricles rather than by the sinoatrial nodePVCs may cause no symptoms or may be perceived as a "skipped beat" or felt as palpitations in the chest Single beat PVCs do not usually pose a danger The electrical events of the heart detected by theThe vagus nerve is an efferent tract from the medulla to the heart, causing sinus bradycardia, junctional rhythm, AV block, bigeminy, and nodal beats Bradycardia can also progress to sinus arrest, asystole, or ventricular fibrillation 3–7,10 An episode of the OCR may lead to bradycardia terminating in asystole or to asystole with no

Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
Sinus bradycardia with unifocal ventricular bigeminy
Sinus bradycardia with unifocal ventricular bigeminy-Sinus Rhythm with wide QRS and Bigeminy, Unifocal Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) if stated rate is 100 or Sinus Bradycardia with wide QRS and Bigeminy, Unifocal PVC's if stated rate is 50 (would not have wide QRS if 012) 1/1/ 7 Regular Rate 80 P waves sawtooth/flutter3 paroxysms of atrial fibrillation initiated by closely coupled APBs




Float Nurse Basic Ekg Rhythm Test 39
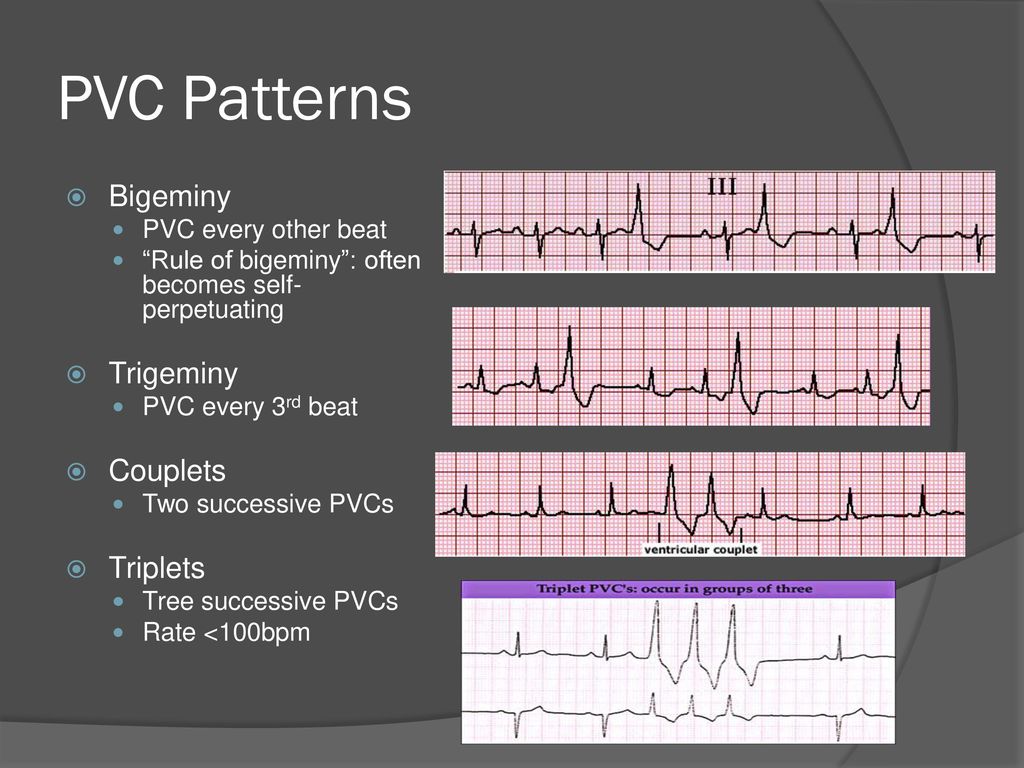
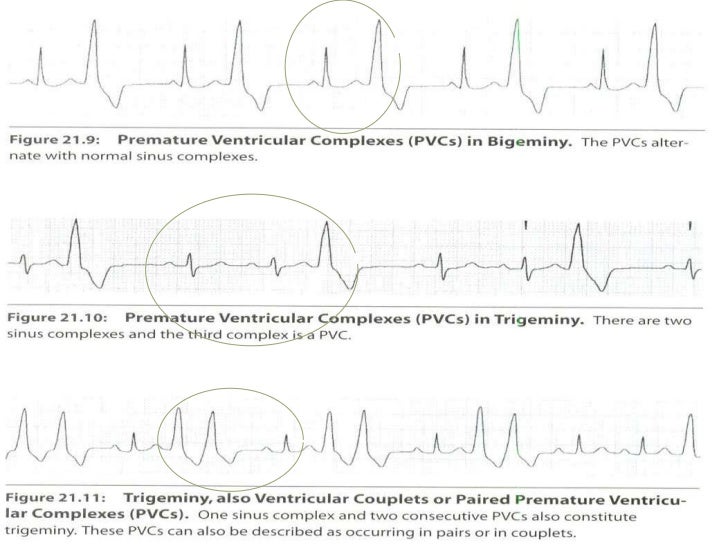
It is perfectly appropriate to call this something very descriptive like "sinus tachycardia with a unifocal PVC every third beat", but this rhythm is often called sinus tachycardia with ventricular trigeminy If every second complex was a PVC, it can be called bigeminy It is important to compare the peripheral pulse rates to the EKGVentricular bigeminy – Ventricular bigeminy, with ventricular premature beats occurring every other beat, may occasionally be associated › Sinus bradycardia cause a low heart rate, for example, ventricular bigeminy where the PVC beats result in diminished cardiac output In the case of this ineffective bigeminy, a falsely low heart rate canUnifocal VEBs arising from the right ventricular outflow tract are common and may increase with exercise and cause non‐sustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia Catheter ablation is effective and safe treatment for these patients β blockers may be used for symptom control in patients where VEBs arise from multiple sites
EKGStrips Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free · Sinus bradycardia is a slow, regular heartbeat It happens when your heart's pacemaker, the sinus node, generates heartbeats less than 60 times in a minute For some people, such as healthy youngVentricular Rhythms Complete presentation of Unifocal Premature Ventricular Contractions (Unifocal PVCs), Multifocal Premature Ventricular Contractions (Multifocal PVCs), Ventricular Bigeminy, Ventricular Trigeminy, Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation, and Ventricular Asystole (Cardiac Standstill) This section concludes with a
Ventricular Tachycardia (VTach) This is a very serious arrhythmia Whenever three or more consecutive PVS's are seen, at a rate of 100 bpm or more, the term used is Ventricular Tachycardia (V Tach) In the strictest definition, V Tach is the sameBradycardia Bradycardia is the opposite of tachycardia When the heart rate is too slow, say less than 50 beats per minute, the child is likely to have bradycardia momjunctioncom Ventricular tachycardia (,7,27,8 11 cases) 4 Premature ventricular beats (23,4) and bigeminy (4) 5Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 1) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 2) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 3) Sinus Bradycardia ECG (Example 4) Sinus Tachycardia ECG (Example 1) Sinus Tachycardia ECG




Electrocardiographic Monitoring Various Rhythms And Dysrhythmias Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular Tachycardia Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Supraventricular Ppt Download




Ecg Educator Blog Ventricular Bigeminy
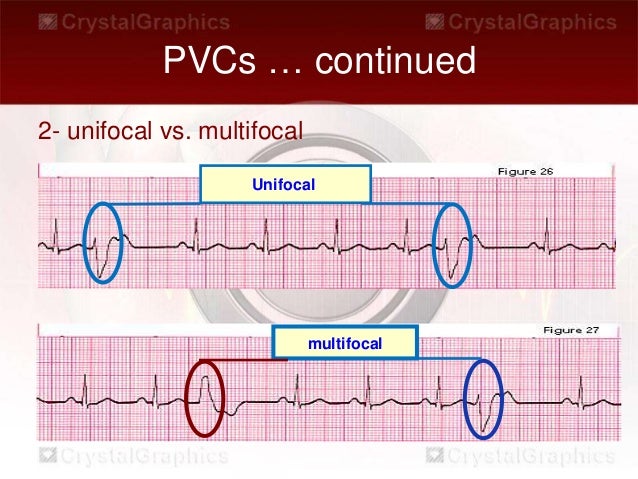
· Unifocal — arising from a single ectopic focus; · ECG BASICS Sinus Rhythm With Ventricular Bigeminy Nice, clear example of ventricular bigeminy with an underlying sinus rhythm We do not know from this strip if the sinus rhythm is a bradycardia at a rate of about 42 per minute, or if the underlying sinus rhythm is actually at a rate of 85 per minute, with every other sinus beat inhibited by the · 01 d Sinus tachycardia 02 a Atrial fibrillation with a multifocal triplet of PVCs 03 c NSR with multifocal PVCs NSR with PVC followed by a ventricular escape beat, The first complex is a fusion complex or an aberrantly conducted PAC It looks like a PVC but it is preceded by a P wave 04 d NSR with multifocal PVCs 05 c Ventricular




Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ecgs Arrhythmias Abnormal Cardiac Rhythms Prompt Assessment Of
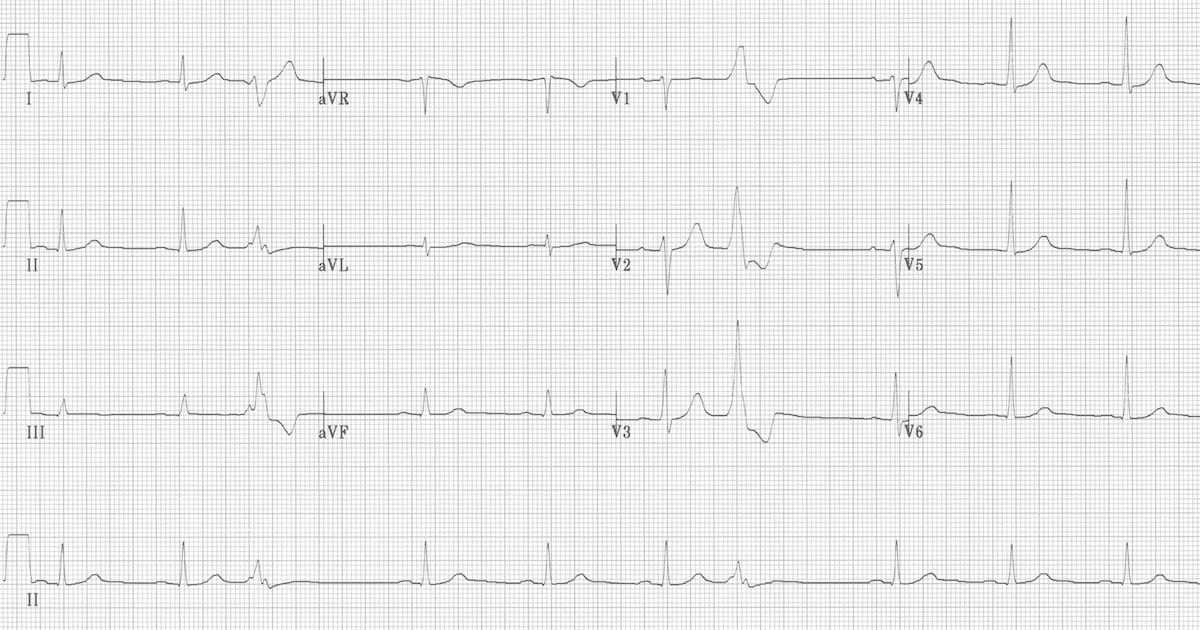
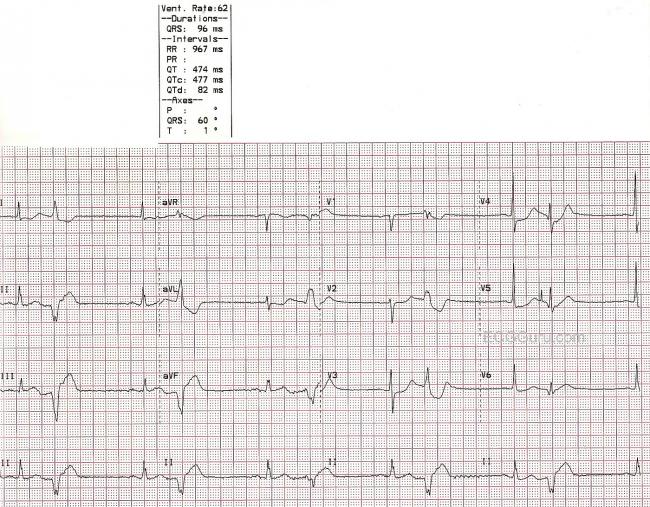
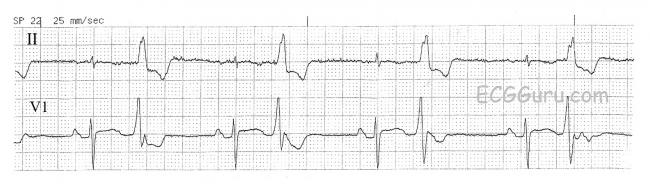
· Sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs 12 Identify the following rhythm a Atrial fibrillation b Atrial flutter Sinus bradycardia Identify the following rhythm a Sinus arrhythmia b Sinus exit block Sinus rhythm with bigeminal PVCs 29 b Complete heart block 30 c Sinus rhythm with a dropped PAC atInterpretation Sinus bradycardia with (unifocal) ventricular bigeminy Rhythm Strip #3 ECG Criteria Heart rate Rhythm P waves PR interval QRS widthBigeminy is a cardiac arrythmia in which there is a single ectopic beat, or irregular heartbeat, following each regular heartbeat Most often this is due to ectopic beats occurring so frequently that there is one after each sinus beat, or normal heartbeat The two beats are figuratively similar to two twins For example, in ventricular bigeminy, a sinus beat is shortly followed by a premature ventricular contraction, a pause, another normal beat, and then another PVC In atrial bigeminy,




Ekg Interpretation




Ekg Interpretation
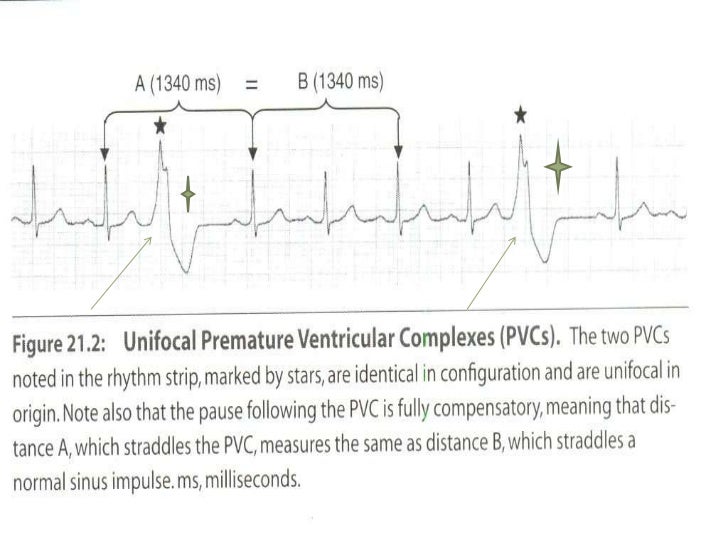
Heart rate (ventricular rate) is bradycardic (49/minute) but this is not sinus bradycardia since P wave rate (atrial rate) is 98/minute Atrial rate is normal but its conduction to the ventricles is the problem ECG machine inadvertently reported it as sinus bradycardiaEach PVC is identical;11 EKG/ECG Certification Study Guide For EM NurseOnFire $2299 Understanding EKG Strips 58 terms kgar_17 EKG examples from the slide decks 38 terms




Bigeminy Wikipedia




Arrhythmias
ECG BASICS Sinus Rhythm With Ventricular Bigeminy Nice, Ventricular beats may be unifocal or multifocal an elderly woman with diuretictreated heart failure taking more than 1 potentially QTprolonging drug with sinus bradycardia and occasional ventricular ahajournalsorg · Causes of Bigeminy There can be many causes of bigeminy, such as Heart disease;2 intermittent atrial bigeminy with block towards the ventricles (this rhythm mimicked sinus bradycardia with ventricular rates of 3845 beats/min and the ectopic P waves were visible on only one of the ECG channels);




Premature Ventricular Complexes Medictests




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography
Sinus bradycardia View in Chinese recorded with a plethysmograph system, other conditions can cause a low heart rate, for example, ventricular bigeminyPseudobradycardias manifesting as slow peripheral pulse rates can result from frequent, nonconducted early atrial premature beats, from ventricular bigeminy or runs of ventricular extrasystoles or from mechanical alternans Cardiac pacemakers play an important role in the management of patients with severe symptoms attributable to bradyarrhythmiasSinus bradycardia ECG, causes & management Definition of sinus bradycardia Sinus bradycardia fulfills the criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is slower than 50 beats per minute ECG criteria follows Regular rhythm with ventricular rate slower than 50 beats per minute Pwaves with constant morphology preceding every QRS complex
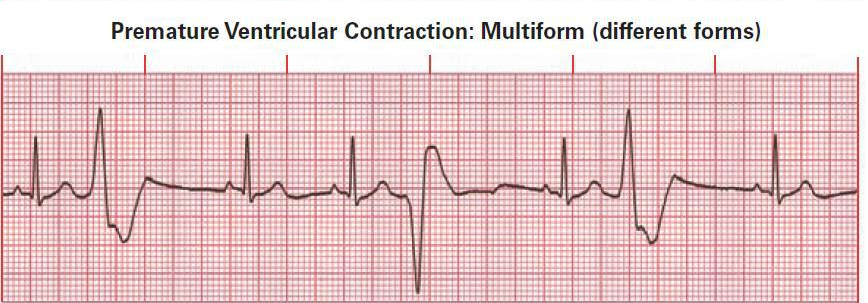



Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn




Vpcs
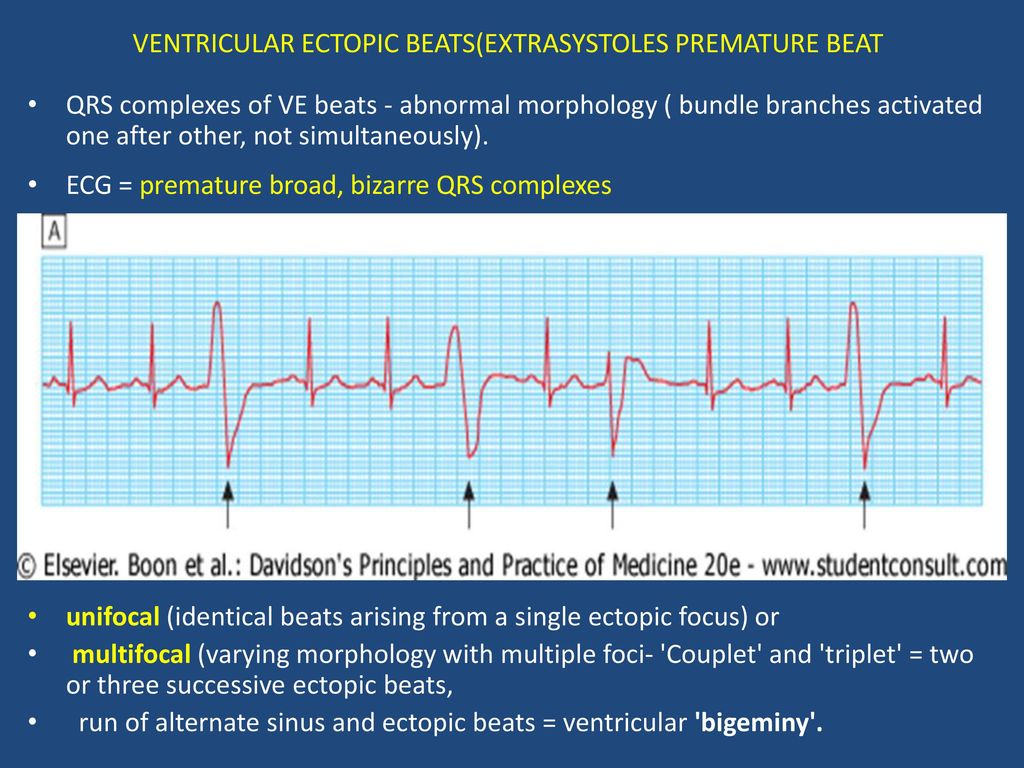
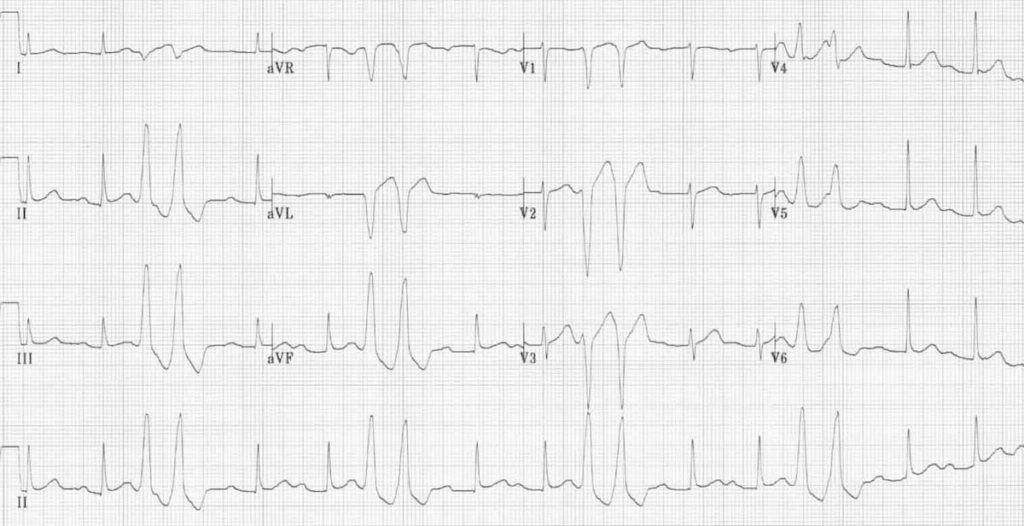
· 02 d Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response 03 a Sinus rhythm with bigeminal PACs 04 b Sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs · View Test Prep quizlet EKGpdf from NURS DDD at Baptist Health College Little Rock Atrial Flutter First Degree AV Block Junctional Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Second Degree AVThe origin of each PVC can be discerned from the QRS morphology PVCs arising from the right ventricle have a left bundle branch block morphology (dominant S wave in V1)




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Ecg Interpretation Of Arrhythmias Tusom Pharmwiki
· Ventricular paced with failure to capture 05 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs b Junctional rhythm with unifocal PVCs c Sinus tachycardia with unifocal PVCs dThis encounter shows a normal sinus rhythm with a large amount of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), evolving into a phenomenon known as bigeminy This is when a pattern of one normal beat followed by one ectopic beat develops In this case, the ectopic beat is a PVC Source PhysioNet MGH107 · Of interest was that his ECG now displayed marked sinus bradycardia with frequent premature ventricular contractions in a bigeminy pattern His ventricular rate, including bigeminy, was 70 bpm Discounting the confounding premature ventricular contractions, his heart rate was 38 bpm
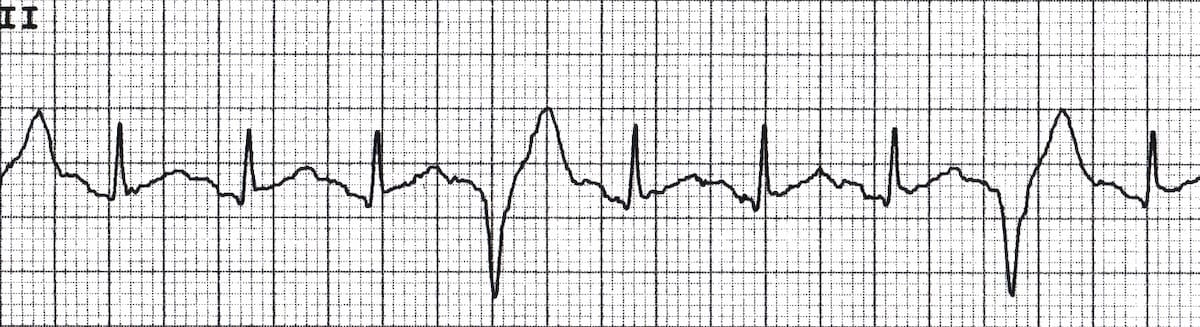



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
In addition, sinus bradycardiawith a rate Arrhythmia consists of ventricular bigeminy and runs of unifocal and multifocal ventricular complexes ferentsurgicalprocedureAnalysisofstrip4 ofFig 3 reveals the previously mentioned late diastolic bigeminy The origin of the ectopic complexes isView Normal Sinus Rhythmdocx from NURSING 316 at Richard J Daley College, City Colleges of Chicago Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Bradycardia Sinus tachycardia w unifocal PVCs Sinus · Bigeminy or bigemini is a heart rhythm problem in which there is a continuous alternation of long and short heart beatsMost often this is due to ectopic beats occurring so frequently that there is one after each sinus beat The two beats are figuratively two twins (hence bi gemini)The ectopic beat is typically a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
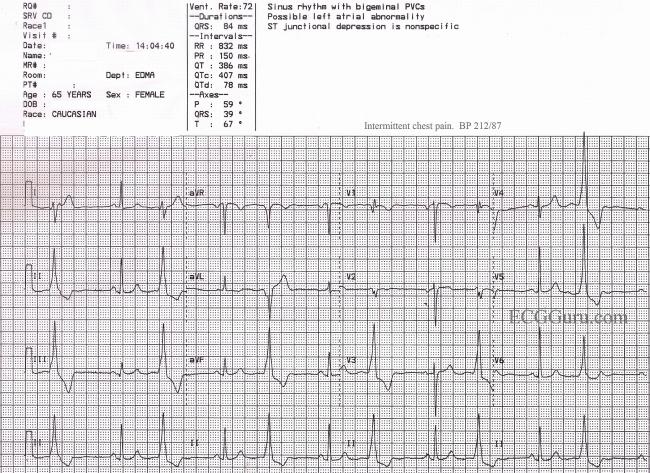



Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Search Q Ventricular Tachycardia Tbm Isch
Causes Sick Sinus Syndrome Causes Heart Block Causes Treatments for Bradycardia If your doctor says you or a loved one has bradycardia, a restingSevere sinus bradycardia, complete sinus arrest, junctional escape rhythm, or ventricular escape rhythm was found in four patients, and permanent multiprogrammable pacemakers ncbinlmnihgov Answers to question 1 The 12lead ECG demonstrated atrioventricular (AV) junctional rhythm with ventricular bigeminyMultifocal — arising from two or more ectopic foci;
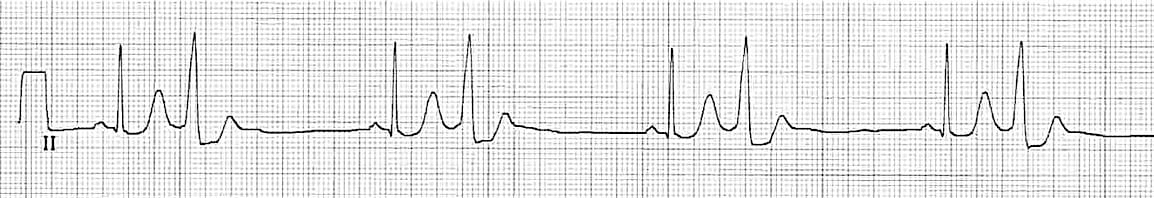



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Arrhythmias Seen In Baseline 24 Hour Holter Ecg Recordings In Healthy Normal Volunteers During Phase 1 Clinical Trials Hingorani 16 The Journal Of Clinical Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
· Section 1 Supraventricular rhythms Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm with a normal U wave Sinus arrhythmia (irregular sinus rhythm) Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Atrial bigeminy Atrial trigeminy Ectopic atrial rhythm Multifocal atrial tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response Atrial fibrillation and bundle branch block AtrialPVCs — also called also called premature ventricular complexes, ventricular premature beats and extrasystoles — are very common and usually harmless Symptoms, Causes and Diagnosis of PVCs Symptoms of PVCs include a fluttering or flipflop feeling in the chest, pounding or jumping heart rate, skipped beats and palpitations, or an increasedSinus bradycardia is a type of slow heartbeat A special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node Normally, the SA node fires at about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest In sinus bradycardia, the node fires less than 60 times per minute




Bigeminy Wikipedia



Www Scripps Org Assets Documents Eval Of Patient With Arrhythmia Rogers Pdf
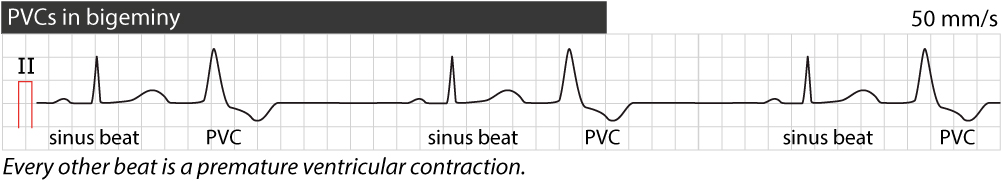
In atrial bigeminy a premature atrial beat beat follows each sinus beat If the PAC is not conducted bradycardia may result; · PVC Practice Strips (class 6) 01 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus rhythm with multiform PVCs b Sinus bradycardia with a trigeminal PVCs c Sinus rhythm with bigeminalWhile this ECG rhythm could be called a sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs, since the PVCs occur every second QRS complex, this ECG rhythm is commonly referred to as ventricular bigeminy Six Second ECG Quiz 3A v31 Annotated Answer Key




Ekg Interpretation



Www oms Org Docs Handouts rc Ekg Lecture Primer Pdf
· We report a case of severe sinus bradycardia with atrial bigeminy and junctional rhythm in the setting of moderate hyperkalemia Case Presentation A 73yearold gentleman with hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, stage 4 chronic kidney disease, heart failure with left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% and hypothyroidism presented withIf it is symptomatic treatment with digitalis or quinidine is indicated Junctional bigeminy may be coupled to sinus beats or may accompany atrial fibrillationThis is a trigeminovagal reflex in response to pressure on the globe or traction on the eye muscles, which most commonly manifests as sinus bradycardia However, other dysrhythmias, including ventricular bigeminy, junctional bradycardia, and sinus arrest, may occur




Pvc Ecg Example 2 Learntheheart Com



Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn
If you have bigeminy (biJEMuhnee), your heart doesn't beat in a normal pattern After every routine beat, you have a beat that comes too early, or what's known as a premature ventricular · Sinus bradycardia occurs on an ECG when there is a normal upright P wave in lead II ― sinus P wave ― preceding every QRS complex with a ventricular · Nice, clear example of ventricular bigeminy with an underlying sinus rhythm We do not know from this strip if the sinus rhythm is a bradycardia at a rate of about 42 per minute, or if the underlying sinus rhythm is actually at a rate of 85 per minute, with every other sinus beat inhibited by the occurance of a PVC




Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Ventricular Arrhythmias Ppt Download




Electrocardiography Diagnosis And Management Of Common Arrhythmias Wsava13 Vin



1




Cardio Week 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvc Boss Rn




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strip Quiz 140




The Electrocardiographic Footprints Of Ventricular Ectopy Sciencedirect




Arrhythmias Seen In Baseline 24 Hour Holter Ecg Recordings In Healthy Normal Volunteers During Phase 1 Clinical Trials Hingorani 16 The Journal Of Clinical Pharmacology Wiley Online Library




Ecg Interpretation Of Arrhythmias Tusom Pharmwiki




Arrhythmias Images Flashcards Quizlet



Arrhythmias Ventricular Arrhythmias Bradyarrhythmias Management Ppt Download



Ekg Rhythm Identification



Adc Bmj Com Content Archdischild 52 5 345 Full Pdf




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360




Ekg Interpretation



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Venticular Rhythms Flashcards Quizlet




Premature Ventricular Complex With A Compensatory Pause 3 2 8 Work Up Download Scientific Diagram




Ecg Interpretation Of Arrhythmias Tusom Pharmwiki




Premature Ventricular Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Frequent Ventricular Extrasystoles Significance Prognosis And Treatment




Float Nurse Basic Ekg Rhythm Test 39



Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360



Premature Ventricular Contractions Premature Ventricular Complex Premature Ventricular Beats Ecg Echo



Vpcs




Slides Show



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Premature Ventricular Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Interpreting Ecgs Lead 2




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360



Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation



Vpcs



Premature Ventricular Contractions Premature Ventricular Complex Premature Ventricular Beats Ecg Echo
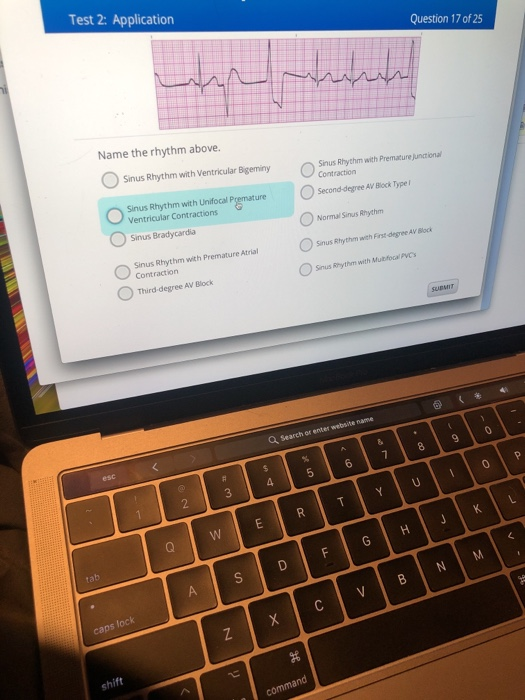



Solved Test 2 Application Question 17 Of 25 Name The Rhy Chegg Com




Rate And Rhythm Premature Ventricular Contraction Pvc Youtube
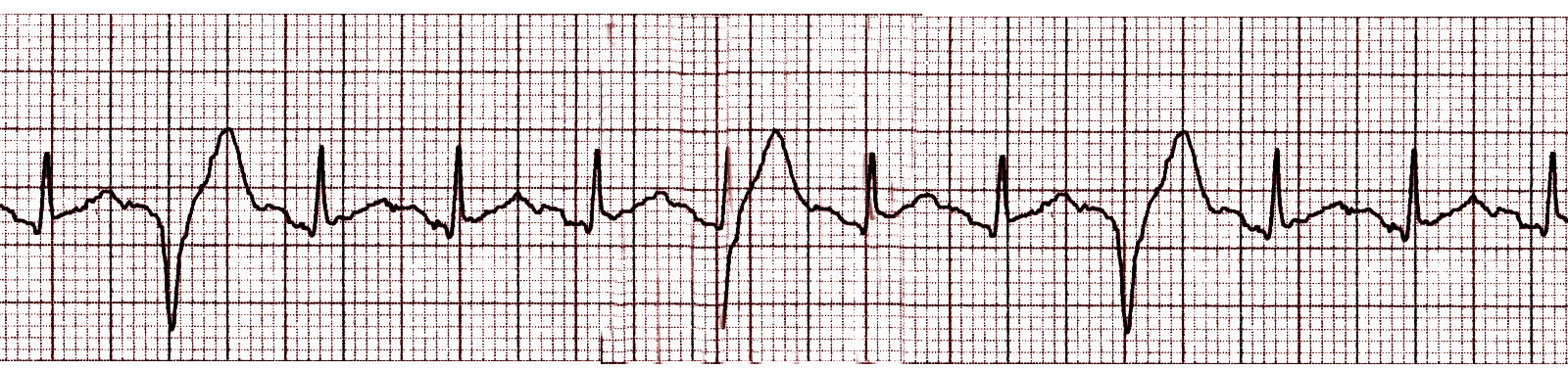



Ventricular Premature Complexes Article




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360




Practice Rhythm Strip 3



Cdn Mdedge Com Files S3fs Public Jfp Archived Issues 1980 Volume 10 11 Jfp 1980 05 V10 I5 Communications Venticular Bigeminy In A Pdf




Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Example 1 Learntheheart Com




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Electrophysiology Of The Heart Ecg Monitoring The Ecg




Electrocardiography Diagnosis And Management Of Common Arrhythmias Wsava13 Vin




Nurs 425 Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet




Ekg Flashcards Quizlet




Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Nurs 108 Spring 08 Majuvy




Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Nurs 108 Spring 08 Majuvy




Premature Ventricular Contraction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Ventricular Arrhythmias Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




Premature Ventricular Contraction Wikipedia




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key




Electrocardiography Diagnosis And Management Of Common Arrhythmias Wsava13 Vin




Ecg Educator Blog Ventricular Bigeminy



Q Tbn And9gcsztx Yiup6dgjcscknsguogls0mjbhalqbp1auz2 K1yzjb3ef Usqp Cau




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Float Nurse March 19



V Fib Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Vtach Ventricular



1




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
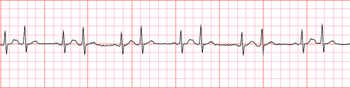



Bigeminy Wikipedia
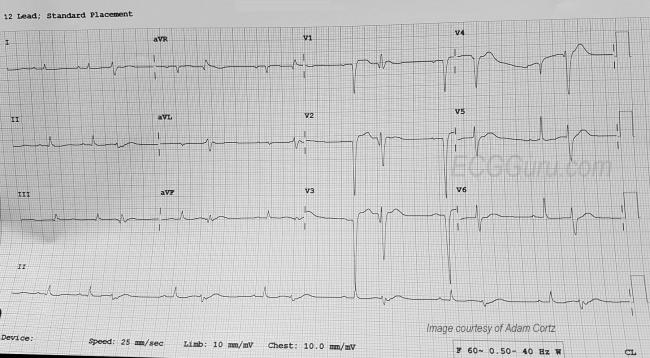



Ventricular Bigeminy Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ecg Shows Ventricular Bigeminy Download Scientific Diagram




Ecgs Arrhythmias Abnormal Cardiac Rhythms Prompt Assessment Of
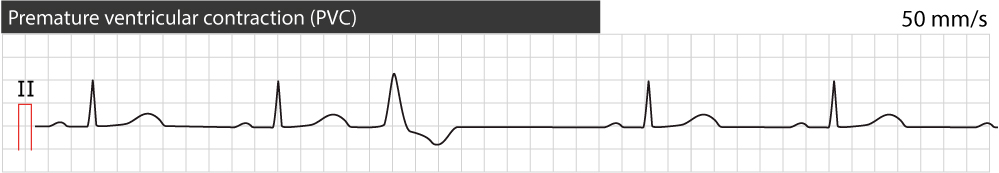



Premature Ventricular Contractions Premature Ventricular Complex Premature Ventricular Beats Ecg Echo
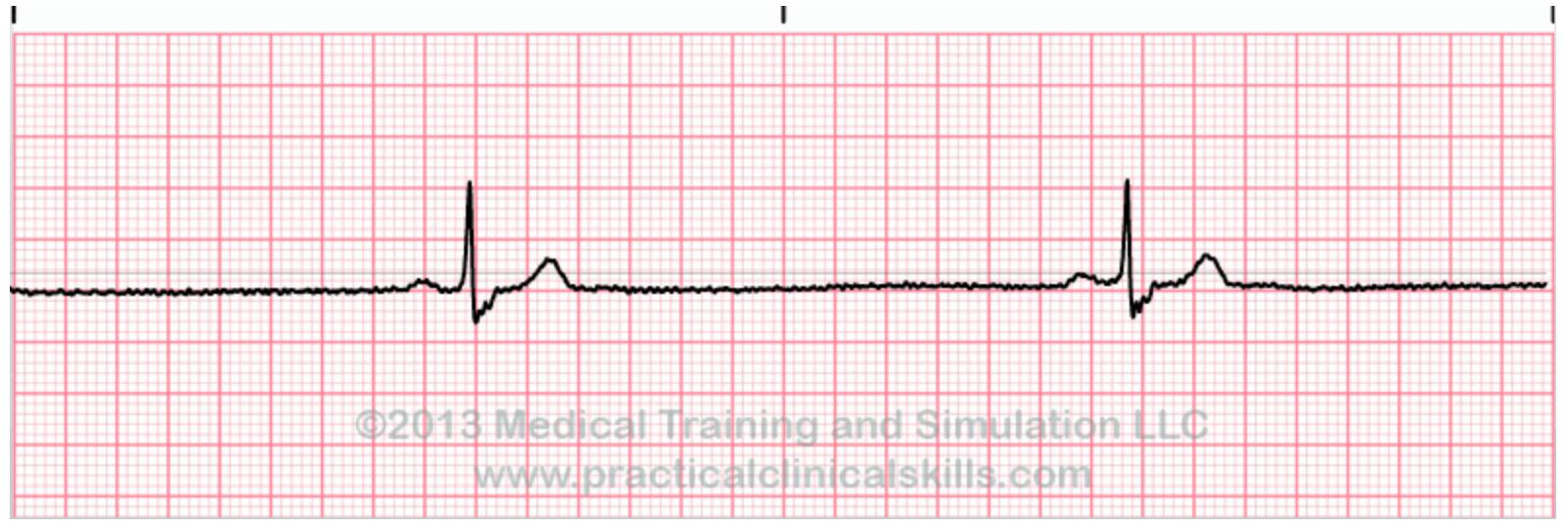



Ekg Flashcards Chegg Com




Bigeminy Wikipedia
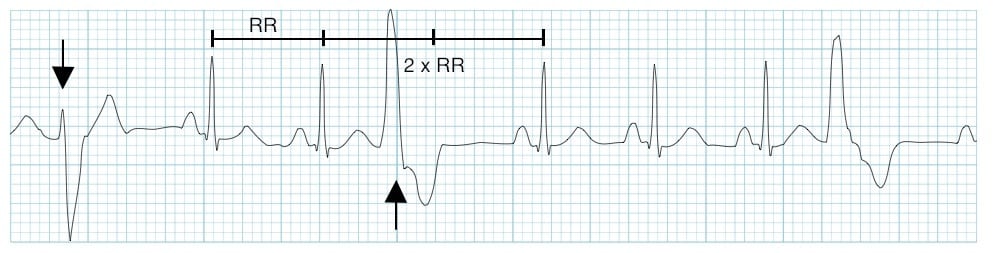



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Cardio Week 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Venticular Rhythms Flashcards Quizlet




Ventricular Arrhythmias Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




Bigeminy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Evaluation And Management Of Ventricular Premature Beats Consultant360


コメント
コメントを投稿